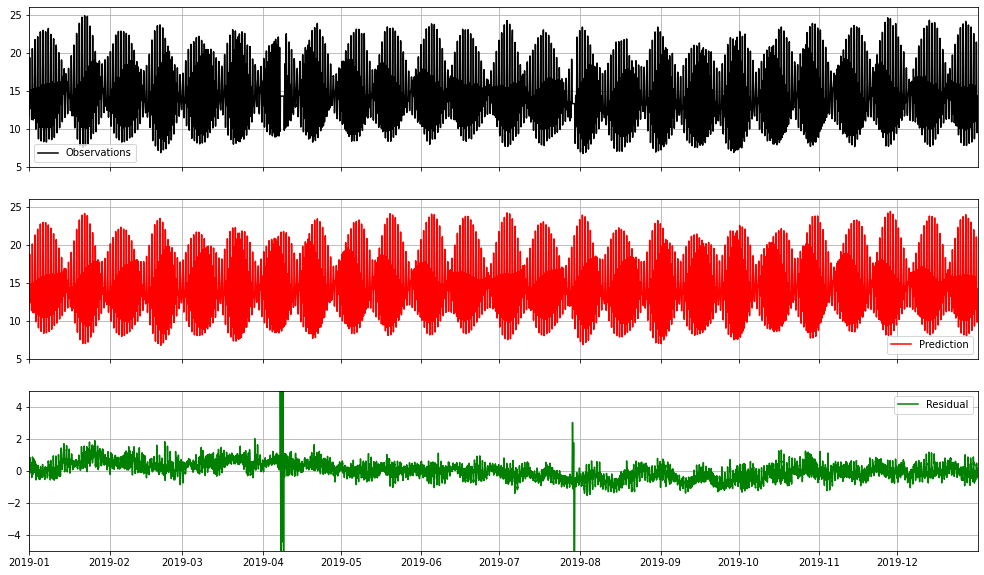
Signal processing is a field that involves the manipulation, analysis, and interpretation of signals to extract valuable information or enhance their quality. It encompasses a range of techniques and methods aimed at processing different types of signals, including audio, images, video, time series data, and more.
In essence, signal processing involves transforming and analyzing signals to uncover patterns, extract relevant features, remove noise or interference, compress data, and make predictions. It enables researchers and practitioners to extract meaningful information from signals, understand their characteristics, and derive valuable insights.
Signal processing techniques include various operations such as filtering, modulation, transformation, compression, and feature extraction. These techniques can be applied to signals in different domains, such as time-domain signals, frequency-domain spectra, or spatial signals.
Signal processing finds applications in numerous fields, including telecommunications, audio and speech processing, image and video processing, biomedical engineering, radar and sonar systems, finance, and more. It plays a vital role in enabling efficient data analysis, facilitating decision-making, and advancing technologies in various domains.
By utilizing signal processing techniques, researchers and practitioners can unveil hidden information, improve signal quality, detect patterns, classify data, and develop models for prediction and estimation. It forms the foundation for many advanced technologies and innovations, contributing to advancements in diverse fields and driving progress in the digital era.
The main goals of signal processing are:
- Signal Representation: Signals are represented using mathematical models or digital representations suitable for analysis and processing. These representations may include time-domain signals, frequency-domain spectra, or other domain-specific representations.
- Filtering and Enhancement: Signal processing techniques are employed to remove unwanted noise, interference, or artifacts from signals. Filtering methods help improve the signal quality by emphasizing desired components or suppressing undesirable components.
- Feature Extraction: Signal processing enables the identification and extraction of meaningful features from signals. These features may include characteristics like amplitude, frequency, duration, or patterns that carry valuable information for further analysis or decision-making.
- Compression: Signal compression techniques reduce the storage space and transmission bandwidth required for signals without significant loss of information. Compression algorithms exploit redundancies or perceptual limitations to achieve efficient representation.
- Analysis and Interpretation: Signal processing enables the analysis of signals to extract relevant information or draw conclusions. This may involve statistical analysis, pattern recognition, machine learning, or other analytical methods tailored to specific signal types and applications.
- Prediction and Estimation: Signal processing can be used to model and predict future signal behavior based on past observations. Time series forecasting, system identification, and estimation techniques are employed to make predictions or estimate unknown signal parameters.
Signal processing finds applications in various fields, including telecommunications, biomedical engineering, radar and sonar systems, geophysics, and many more. It plays a vital role in extracting insights from signals, enabling efficient data analysis, and facilitating decision-making in diverse domains.
